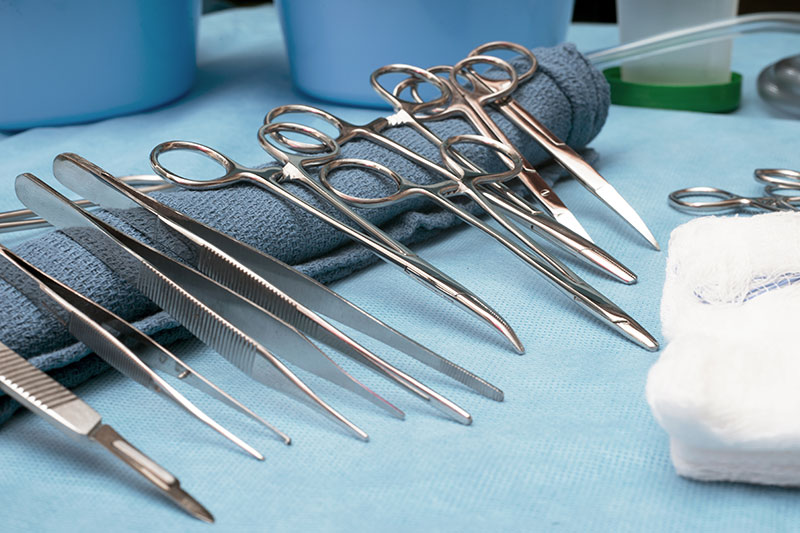
Surgical Instrument Testing
Surgical instrument testing is the process of evaluating the safety, effectiveness, and quality of surgical instruments used in medical procedures. This testing is typically conducted to ensure that surgical instruments meet regulatory requirements, such as those set by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and to ensure that they are safe for patients and healthcare professionals.
Surgical instrument testing may involve a range of different types of tests and evaluations, depending on the specific instrument being tested. Some examples of tests that may be conducted during surgical instrument testing include:
Biocompatibility testing: This involves evaluating the potential of a surgical instrument to cause a biological response in the body, such as inflammation or toxicity.
Mechanical testing: This involves testing the durability and functionality of a surgical instrument under various conditions, such as repeated use or exposure to sterilization methods.
Sterility testing: This involves testing the effectiveness of sterilization methods in eliminating microorganisms from surgical instruments, to prevent the spread of infection.
Performance testing: This involves evaluating the performance of a surgical instrument during actual surgical procedures, to ensure that it performs as intended and does not pose a risk to patients.
Surgical instrument testing is important for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of surgical procedures, and for preventing the spread of infection in healthcare settings. It is typically carried out by specialized testing laboratories, and may be required by regulatory agencies before surgical instruments can be approved for use in medical procedures.
Types of Equipment used
- Horiba

EIA Studies
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies are comprehensive assessments of the potential environmental impacts of a proposed project or development. The purpose of EIA studies is to identify, predict, and evaluate the potential environmental effects of a proposed project or development, and to recommend measures to mitigate or manage any adverse impacts.
EIA studies typically involve a multi-disciplinary approach and may include a range of activities, such as:
Baseline studies: This involves gathering data on the current environmental conditions of the proposed project site, including flora, fauna, soil, air and water quality.
Impact identification and assessment: This involves identifying and assessing the potential environmental impacts of the proposed project or development. The impacts may include physical, chemical, biological, and socio-economic effects.
Mitigation measures: This involves recommending measures to avoid, minimize, or mitigate the adverse environmental impacts of the proposed project. This may include engineering or design changes, as well as management plans and monitoring programs.
Environmental management plans: This involves developing plans for the management and monitoring of the environmental impacts of the proposed project over its entire life cycle.
Public participation: This involves engaging stakeholders, including local communities, NGOs and government agencies in the EIA process and considering their concerns and suggestions.
EIA studies are important for ensuring that proposed projects or developments are environmentally sustainable and meet legal requirements. They are typically required by regulatory authorities before a project can proceed, and may also be conducted voluntarily by project proponents to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable development. The EIA process helps to promote environmental protection, sustainability and better decision-making by ensuring that the potential environmental impacts of a project are considered early in the planning process.


IEE Studies
Initial Environmental Examination (IEE) studies are a simplified version of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) studies. They are typically conducted for smaller and less complex projects that are likely to have minimal environmental impacts.
IEE studies are similar to EIA studies in that they involve a systematic evaluation of the potential environmental impacts of a proposed project. However, they are less detailed and typically focus on the most significant environmental impacts of the project.
IEE studies may involve activities such as:
Baseline studies: This involves gathering data on the current environmental conditions of the proposed project site, including flora, fauna, soil, air and water quality.
Impact identification and assessment: This involves identifying and assessing the potential environmental impacts of the proposed project or development. The impacts may include physical, chemical, biological, and socio-economic effects.
Mitigation measures: This involves recommending measures to avoid, minimize, or mitigate the adverse environmental impacts of the proposed project. This may include engineering or design changes, as well as management plans and monitoring programs.
Environmental management plans: This involves developing plans for the management and monitoring of the environmental impacts of the proposed project over its entire life cycle.
IEE studies are important for ensuring that smaller and less complex projects are environmentally sustainable and meet legal requirements. They are typically required by regulatory authorities before a project can proceed, and may also be conducted voluntarily by project proponents to demonstrate their commitment to sustainable development. The IEE process helps to promote environmental protection, sustainability and better decision-making by ensuring that the potential environmental impacts of a project are considered early in the planning process.